Baidu; Deep Bench Optimization for Deep Learning
At the O’Reilly Artificial Intelligence conference on September 29, 2016, Baidu Research announced DeepBench, an open source benchmarking tool for evaluating the performance of deep learning operations on different hardware platforms. Greg Diamos and Sharan Narang of Baidu Research’s Silicon Valley AI Lab talked at the conference about the motivation for developing the benchmark and why faster computers are crucial to the continued success of deep learning.
The harbinger of the current AI Spring, deep learning is a machine learning method using “artificial neural networks,” moving vast amounts of data through many layers of hardware and software, each layer coming up with its own representation of the data and passing what it “learned” to the next layer. As a widely publicized deep learning project has demonstrated four years ago, feeding such an artificial neural network with images extracted from 10 million videos can result in the computer (in this case, an array of 16,000 processors) learning to identify and label correctly an image of a cat. One of the leaders of that “Google Brain” project was Andrew Ng, who is today the Chief Scientist at Baidu and the head of Baidu Research.
Research areas of interest to by Baidu Research include image recognition, speech recognition, natural language processing, robotics, and big data. Its Silicon Valley AI Lab has deep learning and systems research teams that work together “to explore the latest in deep learning algorithms as well as find innovative ways to accelerate AI research with new hardware and software technologies.”
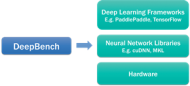
DeepBench is an attempt to accelerate the development of the hardware foundation for deep learning, by helping hardware developers optimize their processors for deep learning applications, and specifically, for the “training” phase in which the system learns through trial and error. “There are many different types of applications in deep learning—if you are a hardware manufacturer, you may not understand how to build for them. We are providing a tool for people to help them see if a change to a processor [design] improves performance and how it affects the application,” says Diamos. One of the exciting things about deep learning for him (and no doubt for many other researchers) is that “as the computer gets faster, the application gets better and the algorithms get smarter.”
Case in point is speech recognition. Or more specifically, DeepSpeech, Baidu Research’s “state-of-the-art speech recognition system developed using end-to-end deep learning.” The most important aspect of this system is its simplicity, says Diamos, with audio on one end, text on the other end, and a single learning algorithm (a recurring convolutional neural network), sitting in the middle. “We can take exactly the same architecture and apply it to both English and Mandarin with greater accuracy than systems we were building in the past,” says Diamos.
In Mandarin, the system is more accurate in transcribing audio to text than native speakers, as the latter may have difficulty understanding what is said because of noise level or accent. Indeed, the data set used by DeepSpeech is very large because it was created by mixing hours of synthetic noise with the raw audio, explains Narang. The largest publicly available data set is about 2000 hours of audio recordings while the one used by DeepSpeech clocks in at 100,000 hours or 10 terabytes of data.
Category: Uncategorized






